A Comprehensive Guide To Acne Management: Understanding, Treating, And Preventing Breakouts
A Comprehensive Guide to Acne Management: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing Breakouts
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Acne Management: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing Breakouts
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Acne Management: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing Breakouts. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Acne Management: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing Breakouts

Acne vulgaris, commonly referred to as acne, is a prevalent skin condition affecting millions worldwide. Characterized by the appearance of pimples, whiteheads, blackheads, and cysts, acne arises from a complex interplay of factors, including hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and environmental influences. While acne can be frustrating and impact self-esteem, it is a treatable condition with a range of effective strategies. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of acne, exploring its causes, treatment options, and preventative measures to promote clear, healthy skin.
Understanding the Roots of Acne:
Acne originates within the hair follicles, the tiny pores that house hair shafts. These follicles are lined with sebaceous glands, which produce sebum, a natural oil that lubricates the skin. When excess sebum, dead skin cells, and bacteria combine within the follicle, they can form a blockage, leading to the development of acne lesions.
The Role of Hormones in Acne Development:
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly those associated with puberty, menstruation, and pregnancy, play a significant role in acne. During these periods, the body produces increased levels of androgen hormones, which stimulate sebaceous gland activity, leading to heightened sebum production.
The Impact of Genetics on Acne:
Genetic predisposition also influences acne susceptibility. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of acne are more likely to experience the condition themselves.
Environmental Factors Contributing to Acne:
Environmental factors can also contribute to acne development. Excessive exposure to humidity, heat, and pollution can exacerbate existing acne or trigger new breakouts. Friction from tight clothing, backpacks, or helmets can also irritate the skin and worsen acne.
Types of Acne Lesions:
Acne presents itself in various forms, each with distinct characteristics:
- Comedones: These are the most common type of acne lesion and appear as small, flesh-colored bumps. They can be either open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads). Blackheads are open comedones with a dark appearance due to the oxidation of melanin in the sebum plug. Whiteheads are closed comedones with a white or yellowish color, blocked by a layer of skin.
- Papules: These are small, inflamed, red bumps that are tender to the touch.
- Pustules: These are pus-filled bumps that appear red and inflamed.
- Nodules: These are larger, deeper, and more painful lesions that can be red or purple.
- Cysts: These are the most severe form of acne, characterized by large, painful, pus-filled lesions that can leave scars.
Acne Treatment Strategies:
Treatment for acne is tailored to the individual’s specific needs, considering the severity of the condition and the types of lesions present. Common treatment approaches include:
1. Topical Medications:
- Retinoids: Retinoids are derivatives of vitamin A that help unclog pores, reduce inflammation, and regulate sebum production. They are available in various strengths and formulations, including creams, gels, and lotions.
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This over-the-counter medication kills bacteria that contribute to acne and helps reduce inflammation. It is available in various concentrations, with higher concentrations generally more effective but potentially more irritating.
- Salicylic Acid: This beta-hydroxy acid (BHA) works by exfoliating the skin and unclogging pores. It is available in a range of products, including cleansers, toners, and spot treatments.
- Sulfur: Sulfur is a drying agent that helps reduce sebum production and inflammation. It is often found in acne-fighting masks and spot treatments.
2. Oral Medications:
- Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics are prescribed to fight bacteria that contribute to acne. They are typically used in conjunction with topical medications.
- Hormonal Therapies: For women, hormonal therapies, such as birth control pills, can help regulate hormone levels and reduce sebum production.
- Isotretinoin (Accutane): This powerful oral medication is reserved for severe, recalcitrant acne that does not respond to other treatments. It works by reducing sebum production and decreasing inflammation.
3. Professional Treatments:
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels use acids to remove the outer layers of skin, promoting cell renewal and reducing acne scars.
- Microdermabrasion: This procedure uses a handheld device to exfoliate the skin and remove dead skin cells, improving the appearance of acne scars.
- Laser Therapy: Laser therapy can reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and stimulate collagen production, improving the appearance of acne scars.
4. Lifestyle Modifications:
- Maintaining a Healthy Diet: While no specific diet can cure acne, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall skin health.
- Managing Stress: Stress can trigger hormonal fluctuations, which can exacerbate acne. Stress management techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can be beneficial.
- Getting Enough Sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and well-being, including skin health. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Avoiding Touching the Face: Touching the face can transfer bacteria and irritants, worsening acne.
- Using Gentle Skin Care Products: Harsh soaps, cleansers, and scrubs can irritate the skin and worsen acne. Opt for gentle, non-comedogenic products.
- Protecting the Skin from the Sun: Excessive sun exposure can worsen acne and contribute to scarring. Wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily.
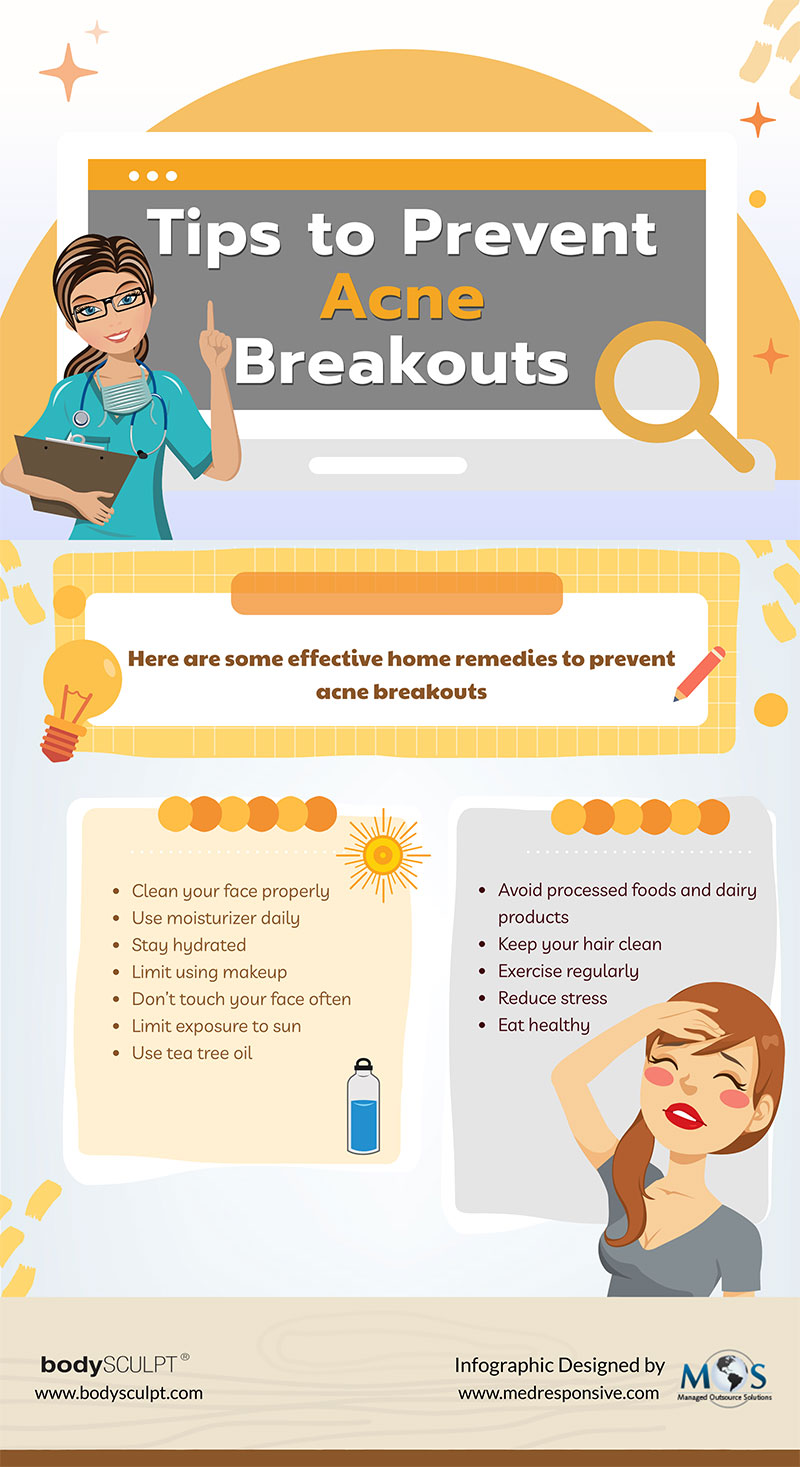
Preventing Acne Breakouts:
While acne is often unavoidable, adopting preventative measures can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of breakouts.
- Washing the Face Twice Daily: Gently cleanse the face twice a day with a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and bacteria.
- Exfoliating Regularly: Exfoliating removes dead skin cells, preventing clogged pores. Use a gentle scrub or chemical exfoliant 1-2 times per week.
- Avoiding Comedogenic Products: Avoid using products that are likely to clog pores, such as heavy moisturizers, oils, and makeup. Look for products labeled as "non-comedogenic."
- Managing Stress: Stress can exacerbate acne. Practice stress management techniques to minimize its impact on your skin.
FAQs on Acne Management:
Q: How long does it take for acne treatments to work?
A: The time it takes for acne treatments to show results varies depending on the severity of the condition and the type of treatment used. Topical medications may take several weeks to show noticeable improvement, while oral medications and professional treatments may take longer.
Q: Can acne be cured?
A: Acne is not typically cured, but it can be effectively managed and controlled. With proper treatment and preventative measures, most people can achieve clear skin and reduce the frequency and severity of breakouts.
Q: Are there any home remedies for acne?
A: While some home remedies, such as applying honey or tea tree oil, may provide temporary relief, they are not proven to be effective in treating acne. It is always best to consult with a dermatologist for personalized treatment recommendations.
Q: Can acne be prevented?
A: While acne is often influenced by genetics and hormonal factors, adopting preventative measures can significantly reduce the likelihood and severity of breakouts.
Q: Can acne cause scarring?
A: Yes, acne can cause scarring, especially if left untreated or if lesions are picked or squeezed. Scarring can range from mild discoloration to deep, pitted scars.
Q: When should I see a dermatologist?
A: It is recommended to see a dermatologist if you have persistent or severe acne, if home remedies are not effective, or if you are concerned about scarring. A dermatologist can provide personalized treatment recommendations and address any underlying concerns.
Tips for Managing Acne:
- Be patient: It takes time for acne treatments to show results. Stick with your treatment plan and consult with your dermatologist if you have any concerns.
- Avoid picking or squeezing pimples: This can worsen inflammation, increase the risk of scarring, and introduce bacteria.
- Use sunscreen daily: Sun exposure can worsen acne and contribute to scarring.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, manage stress, and get enough sleep to support overall skin health.
- Listen to your skin: Pay attention to how your skin reacts to different products and treatments. Adjust your routine as needed.
Conclusion:
Acne is a common skin condition that can be managed effectively with a combination of treatment options and preventative measures. Understanding the causes of acne, exploring available treatment strategies, and adopting a proactive approach to skin care can help individuals achieve clearer, healthier skin. While acne can be frustrating, it is important to remember that it is a treatable condition, and with the right approach, you can regain your confidence and enjoy clear, radiant skin.

![]()

![]()


![]()
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Acne Management: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing Breakouts. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!