The Link Between Sunscreen And Fatigue: Exploring Potential Causes And Solutions
The Link Between Sunscreen and Fatigue: Exploring Potential Causes and Solutions
Related Articles: The Link Between Sunscreen and Fatigue: Exploring Potential Causes and Solutions
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Link Between Sunscreen and Fatigue: Exploring Potential Causes and Solutions. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Link Between Sunscreen and Fatigue: Exploring Potential Causes and Solutions

The sun’s rays, while providing essential vitamin D and promoting a healthy mood, can also be a source of unwanted side effects. One such effect, often reported by individuals, is a feeling of fatigue after sun exposure, even when sunscreen has been applied. This phenomenon, while seemingly contradictory, is not uncommon and can be attributed to various factors, each requiring a nuanced understanding for effective management.
Understanding the Potential Causes:
The sensation of fatigue after sunscreen application can be a complex interplay of multiple factors. While the exact mechanisms are still being researched, several potential contributors have been identified:
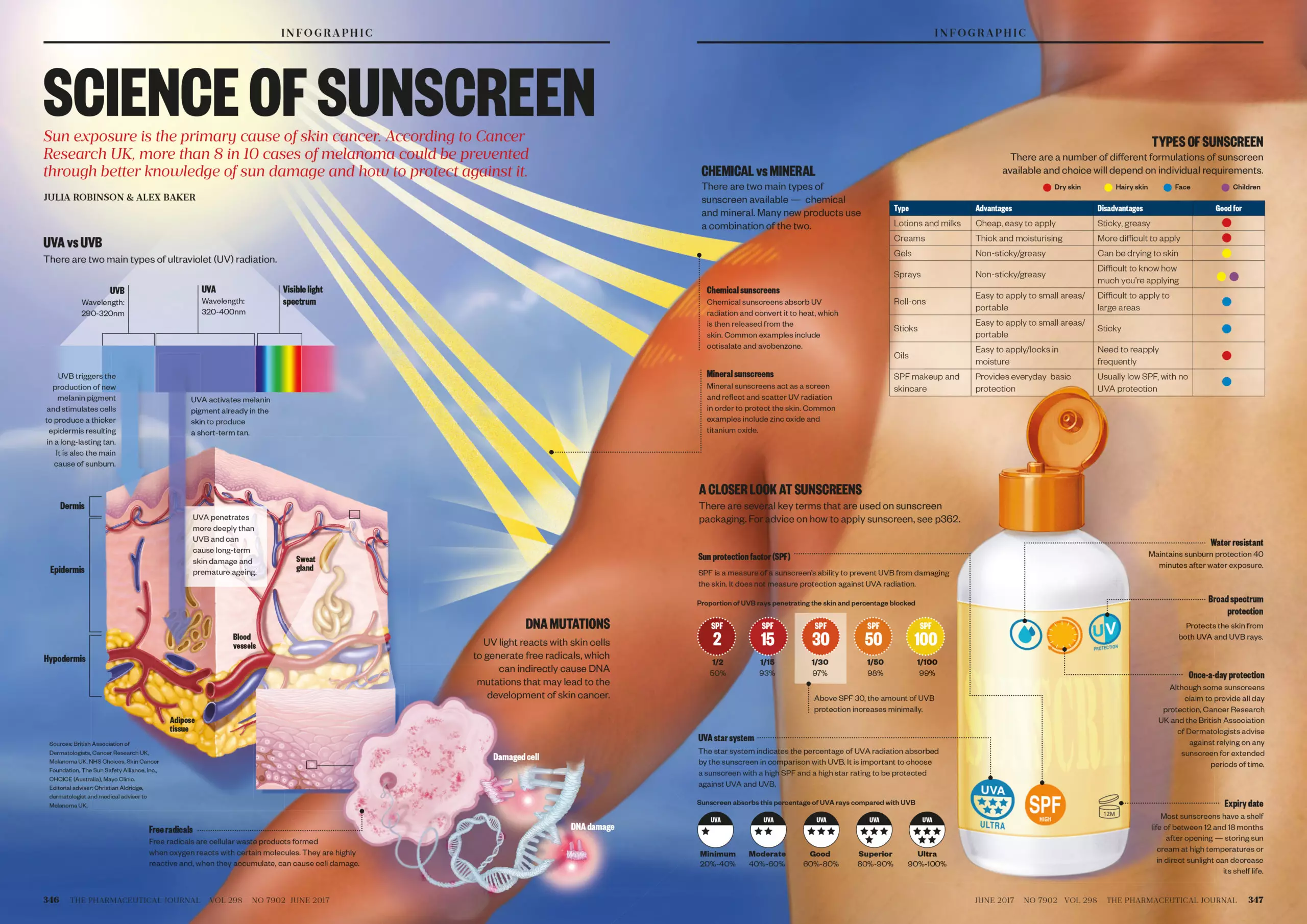
1. Chemical Sunscreen Ingredients:
Certain chemical sunscreen ingredients, such as oxybenzone, octinoxate, and avobenzone, are known to be absorbed into the skin. While they effectively protect against UV radiation, some individuals may experience sensitivity or allergic reactions to these chemicals, leading to fatigue, headaches, or even skin irritation. This is especially true for those with sensitive skin or pre-existing skin conditions.
2. Phototoxicity:
Some sunscreen ingredients, particularly those containing PABA (para-aminobenzoic acid), can cause a reaction known as phototoxicity. This occurs when the ingredient interacts with UV radiation, triggering an inflammatory response in the skin. This inflammation can lead to redness, itching, and a feeling of exhaustion.
3. Dehydration:
Sun exposure can lead to dehydration, which can manifest as fatigue. While sunscreen does protect the skin from UV damage, it does not necessarily prevent water loss through perspiration. Therefore, individuals should remain adequately hydrated, especially during prolonged sun exposure, to mitigate fatigue.
4. Vitamin D Deficiency:
While paradoxical, a deficiency in vitamin D, a nutrient produced by the body through sun exposure, can also contribute to fatigue. Sunscreen, by blocking UV rays, can potentially limit vitamin D synthesis. However, it’s important to note that the amount of time spent in the sun for vitamin D production is minimal and does not preclude the need for sunscreen.
5. Mental Fatigue:
The act of applying sunscreen and being conscious of sun protection can be a mental drain, especially for individuals who are already feeling fatigued. This mental fatigue can be exacerbated by the physical discomfort associated with hot weather, leading to a general sense of exhaustion.
6. Underlying Health Conditions:
Certain underlying health conditions, such as chronic fatigue syndrome, can amplify the feeling of fatigue after sun exposure. These conditions may make individuals more susceptible to the effects of sun exposure, even with sunscreen application.
Addressing Fatigue Associated with Sunscreen Use:
While the exact cause of fatigue after sunscreen application may vary from individual to individual, several strategies can help mitigate this phenomenon:
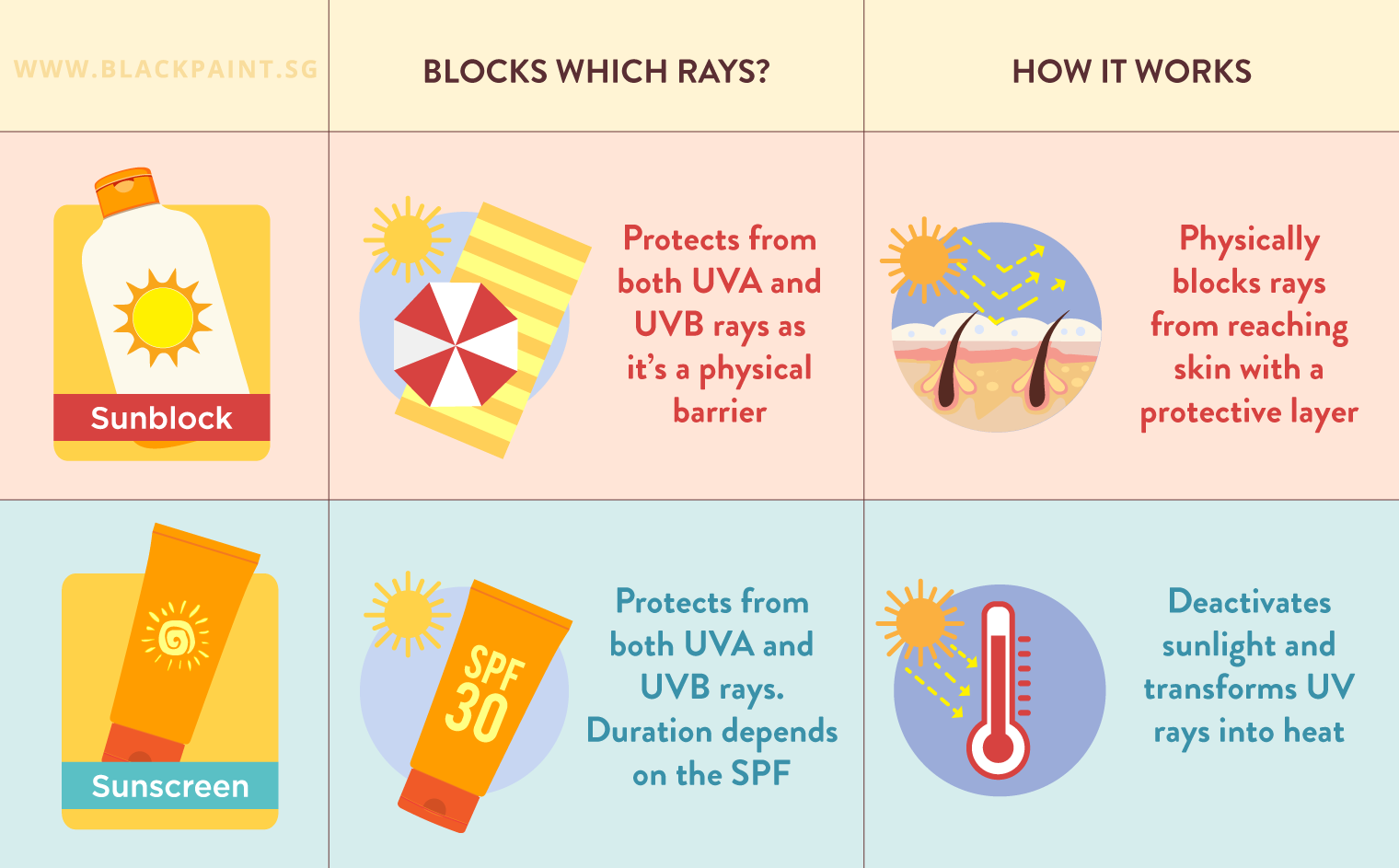
1. Choose Sunscreen Carefully:
Opting for mineral sunscreens, containing ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, is often recommended for sensitive skin. These ingredients are considered gentler and less likely to cause irritation or allergic reactions.
2. Patch Test Before Full Application:
Before applying sunscreen to the entire body, it’s advisable to perform a patch test on a small area of skin. This allows you to assess potential reactions or sensitivities to specific ingredients.
3. Hydration is Key:
Adequate hydration is crucial, especially during prolonged sun exposure. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration, which can contribute to fatigue.
4. Seek Shade and Limit Exposure:
While sunscreen provides protection, it’s essential to limit prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours. Seeking shade whenever possible can further reduce the risk of fatigue.
5. Consider Vitamin D Supplementation:
Individuals concerned about potential vitamin D deficiency due to sunscreen use should consult their healthcare provider about appropriate supplementation. This can help maintain healthy vitamin D levels without compromising sun protection.
6. Address Underlying Health Conditions:
Individuals experiencing persistent fatigue should consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying health conditions. Addressing these conditions can significantly improve overall well-being and reduce the likelihood of fatigue.
7. Manage Mental Fatigue:
Minimize mental fatigue by adopting a relaxed approach to sun protection. Focus on enjoying the outdoors while prioritizing your well-being and ensuring adequate rest.
FAQs:
Q: Is it normal to feel tired after applying sunscreen?
A: While not everyone experiences fatigue after sunscreen application, it is a common enough occurrence that it warrants attention. Several factors can contribute to this phenomenon, and understanding these factors is crucial for effective management.
Q: Does sunscreen make me tired because it blocks vitamin D production?
A: While sunscreen does limit vitamin D synthesis, the amount of time spent in the sun for vitamin D production is minimal. It’s unlikely that sunscreen alone is responsible for vitamin D deficiency, especially if you are already getting enough vitamin D through other sources.
Q: What should I do if I experience fatigue after using sunscreen?
A: First, try to identify potential triggers, such as specific ingredients or environmental factors. If the fatigue persists, consult a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying health conditions.
Q: Can I use sunscreen safely without experiencing fatigue?
A: While fatigue is a possible side effect of sunscreen use, it is not inevitable. By choosing the right sunscreen, minimizing sun exposure, and prioritizing hydration, you can minimize the risk of fatigue while still protecting your skin.
Tips:
- Apply sunscreen generously and evenly, especially on exposed areas.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming or sweating.
- Choose sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher.
- Wear protective clothing, such as hats and sunglasses, to further reduce sun exposure.
- Avoid prolonged sun exposure, particularly during peak hours.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
- Consult a healthcare professional if you experience persistent fatigue or other adverse reactions to sunscreen.
Conclusion:
While sunscreen is essential for protecting the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation, it can sometimes lead to fatigue. Understanding the potential causes and implementing strategies for managing these factors can help individuals enjoy the benefits of sun protection without experiencing undue fatigue. By making informed choices about sunscreen use, prioritizing hydration, and addressing any underlying health concerns, individuals can achieve a healthy balance between sun exposure and well-being.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Link Between Sunscreen and Fatigue: Exploring Potential Causes and Solutions. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!