The Science Of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide To Sunscreen And Skin Health
The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen and Skin Health
Related Articles: The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen and Skin Health
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen and Skin Health. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen and Skin Health

The sun, a vital source of life, also poses a significant threat to human health. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation emitted by the sun can damage skin cells, leading to a range of issues, from premature aging and sunburn to skin cancer. Sunscreen, a crucial tool in protecting the skin from these harmful effects, has evolved significantly, with formulations now designed to be more effective, gentle, and adaptable to diverse skin types. This article delves into the science behind sunscreen, exploring its mechanisms, benefits, and the latest advancements in the field.
Understanding the UV Spectrum and Its Impact on Skin
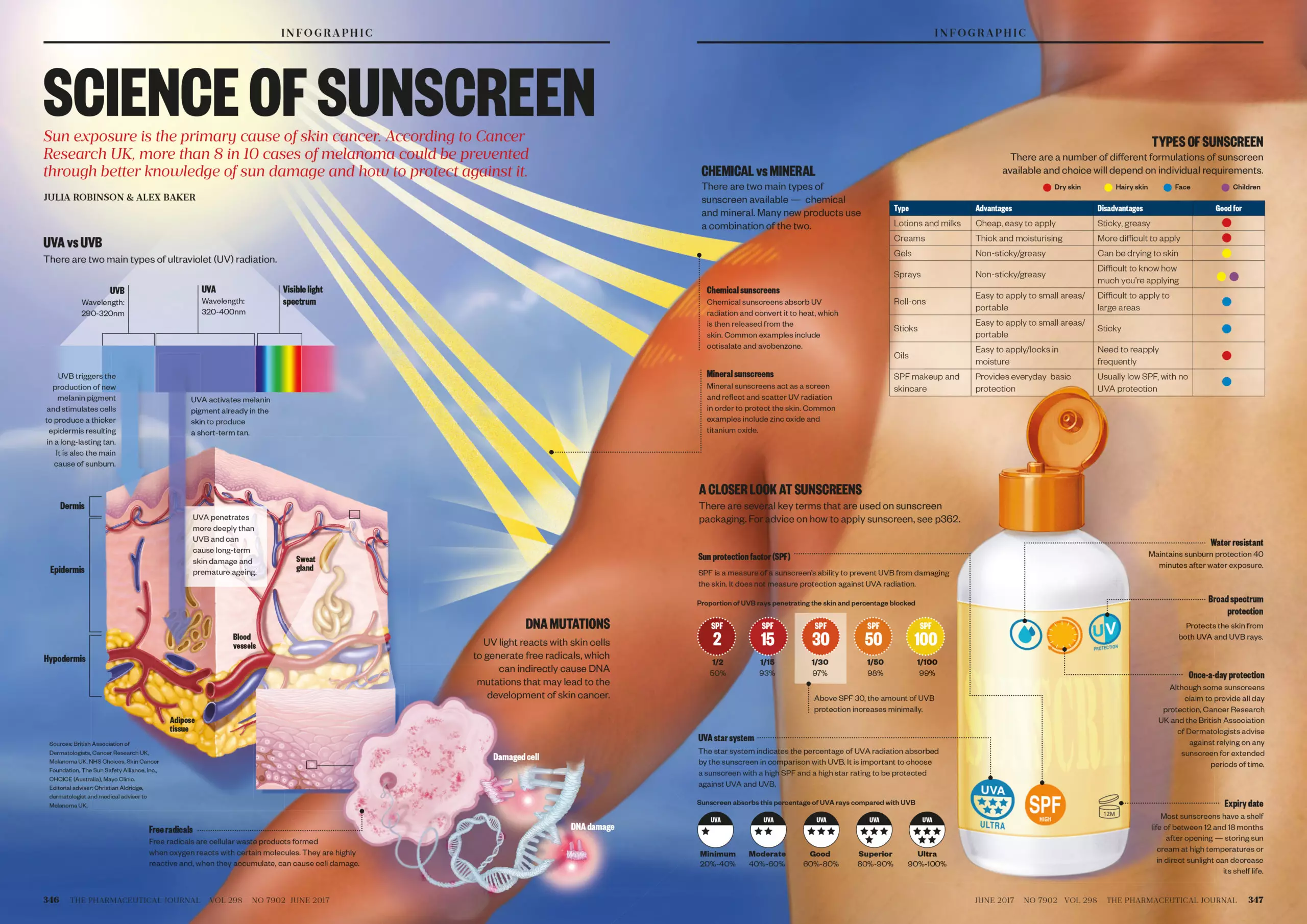
Sunlight comprises various wavelengths of radiation, including ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The UV spectrum is further divided into three categories: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
- UVA (Long-wave UV): UVA rays penetrate deep into the skin, reaching the dermis. They are responsible for premature aging, wrinkles, and contribute to skin cancer development.
- UVB (Medium-wave UV): UVB rays primarily affect the epidermis, the outer layer of the skin. They cause sunburn and play a significant role in skin cancer development.
- UVC (Short-wave UV): UVC rays are absorbed by the ozone layer and do not reach the Earth’s surface.
Sunscreen: A Barrier Against Harmful UV Rays
Sunscreen acts as a protective barrier against UV radiation, absorbing or reflecting these harmful rays before they can reach the skin. There are two main types of sunscreen:
- Chemical Sunscreens: These sunscreens contain specific chemical filters that absorb UV rays and convert them into heat, releasing them from the skin. Common chemical filters include oxybenzone, avobenzone, octinoxate, and octisalate.
- Physical Sunscreens: Also known as mineral sunscreens, these sunscreens use mineral ingredients like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. These minerals sit on the skin’s surface and act as a physical barrier, reflecting UV rays away from the skin.
The Importance of SPF and Broad Spectrum Protection
The effectiveness of sunscreen is measured by its Sun Protection Factor (SPF) and its ability to protect against both UVA and UVB rays.
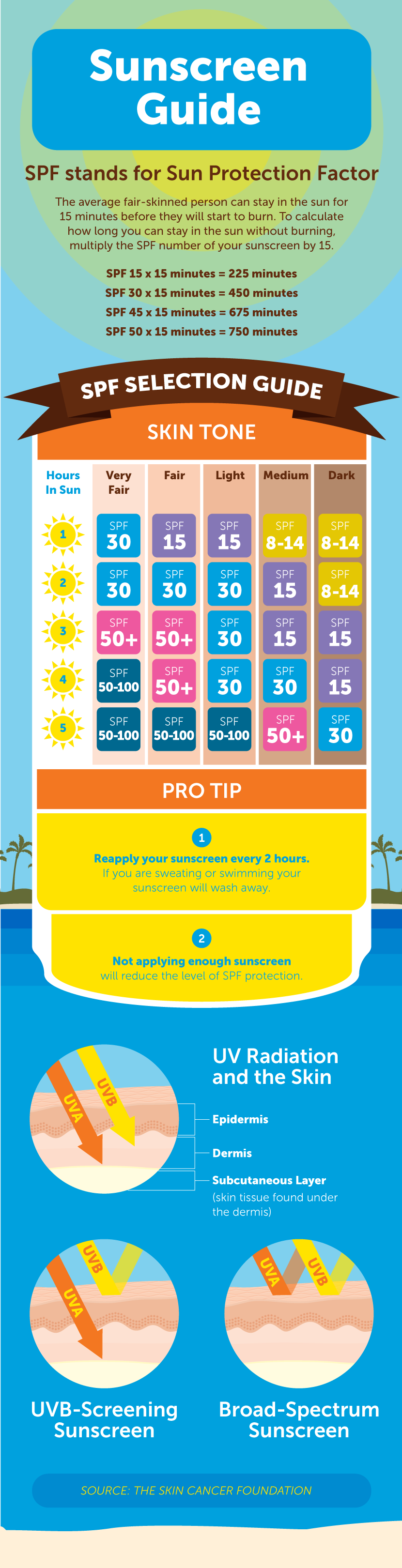
- SPF: SPF indicates how well a sunscreen protects the skin from UVB rays, which cause sunburn. An SPF of 15 means that the skin can be exposed to the sun 15 times longer before experiencing sunburn compared to unprotected skin.
- Broad Spectrum: Broad spectrum sunscreens protect against both UVA and UVB rays. This is crucial for comprehensive skin protection and preventing both sunburn and premature aging.
Factors Influencing Sunscreen Effectiveness
Several factors can affect the effectiveness of sunscreen, including:
- Application: Sunscreen should be applied liberally and evenly to all exposed skin, including the face, neck, ears, and back of the hands.
- Re-application: Sunscreen should be reapplied every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
- Quantity: Most sunscreens require a generous amount – about a teaspoonful for the face and neck, and a shot glass full for the entire body.
- Sun Sensitivity: Individuals with fair skin, a history of sunburn, or certain medical conditions may need to use higher SPF sunscreens and be more diligent with reapplication.
Sunscreen and Skin Health: A Comprehensive Approach
Sunscreen is an essential component of a comprehensive skin health strategy, along with other measures such as:
- Protective Clothing: Wearing protective clothing, including long sleeves, pants, and a wide-brimmed hat, can significantly reduce UV exposure.
- Shade: Seeking shade during peak sun hours (typically between 10 am and 4 pm) can help minimize UV exposure.
- Regular Skin Examinations: Regularly checking your skin for any changes, such as new moles, unusual spots, or changes in existing moles, is crucial for early detection of skin cancer.
Sunscreen: A Vital Ally in Preventing Skin Cancer
Skin cancer is the most common type of cancer in the United States, with over 5 million cases diagnosed annually. Regular sunscreen use is a proven way to reduce the risk of skin cancer development. Studies have shown that individuals who use sunscreen regularly have a significantly lower risk of developing melanoma, the most dangerous form of skin cancer.
The Future of Sunscreen: Innovations and Advancements
Research and development in sunscreen technology are constantly evolving, leading to new and improved formulations. Current advancements include:
- Nano-Sized Particles: Some sunscreens utilize nano-sized particles of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. These smaller particles offer better transparency and spreadability while maintaining effective UV protection.
- Water-Resistant Formulas: Water-resistant sunscreens are designed to remain effective even after swimming or sweating. These formulas are ideal for outdoor activities and water sports.
- Sustainable and Biodegradable Options: Efforts are underway to develop sunscreens with sustainable ingredients and packaging, minimizing their environmental impact.
FAQs about Sunscreen
Q: Is it safe to use sunscreen daily?
A: Daily sunscreen use is recommended for optimal skin health. Sunscreens are generally safe for daily use, with most dermatologists advocating for their regular application.
Q: Does sunscreen expire?
A: Yes, sunscreen does expire. The active ingredients in sunscreen can degrade over time, reducing their effectiveness. Check the expiration date on the bottle and discard any expired sunscreen.
Q: Can I use sunscreen on babies?
A: It is generally safe to use sunscreen on babies over six months old. Choose a sunscreen specifically designed for babies, with a broad spectrum SPF of 30 or higher.
Q: What are the best sunscreens for sensitive skin?
A: Sunscreens formulated for sensitive skin typically use mineral filters like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide, which are less likely to irritate the skin. Look for products labeled "sensitive skin" or "fragrance-free."
Tips for Effective Sunscreen Use
- Apply sunscreen liberally and evenly to all exposed skin, including the face, neck, ears, and back of the hands.
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
- Use a broad spectrum SPF of 30 or higher.
- Choose a sunscreen that is water-resistant if you will be swimming or sweating.
- Store sunscreen in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
- Check the expiration date on the bottle and discard any expired sunscreen.
Conclusion
Sunscreen is an essential tool for protecting the skin from the harmful effects of UV radiation. By understanding the science behind sunscreen, its benefits, and the latest advancements in the field, individuals can make informed decisions about their sun protection practices. From daily use to choosing the right formula for their skin type, embracing a comprehensive approach to sun protection is crucial for maintaining skin health and preventing the long-term consequences of UV exposure. By prioritizing sun safety, we can safeguard our skin and enjoy the benefits of the sun responsibly.





![How does Sunscreen Protect Your Skin from UV Rays [Infographic]](https://www.findatopdoc.com/var/fatd/storage/images/_aliases/infographic_main/beauty-and-anti-aging/how-does-sunscreen-protect-your-skin-from-uv-rays/404933-1-eng-US/How-does-Sunscreen-Protect-Your-Skin-from-UV-Rays.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Science of Sun Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Sunscreen and Skin Health. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!