The Sun’s Embrace: Understanding the Impact of Sunscreen on Skin Health
Related Articles: The Sun’s Embrace: Understanding the Impact of Sunscreen on Skin Health
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Sun’s Embrace: Understanding the Impact of Sunscreen on Skin Health. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Sun’s Embrace: Understanding the Impact of Sunscreen on Skin Health

The sun, a source of life and warmth, also carries a silent threat: ultraviolet (UV) radiation. While moderate sun exposure offers benefits like vitamin D synthesis, excessive exposure can lead to a range of skin issues, from premature aging to severe skin cancer. This is where sunscreen, a crucial shield against the sun’s harmful rays, plays a pivotal role in safeguarding our skin.
The Sun’s Invisible Threat: Understanding UV Radiation
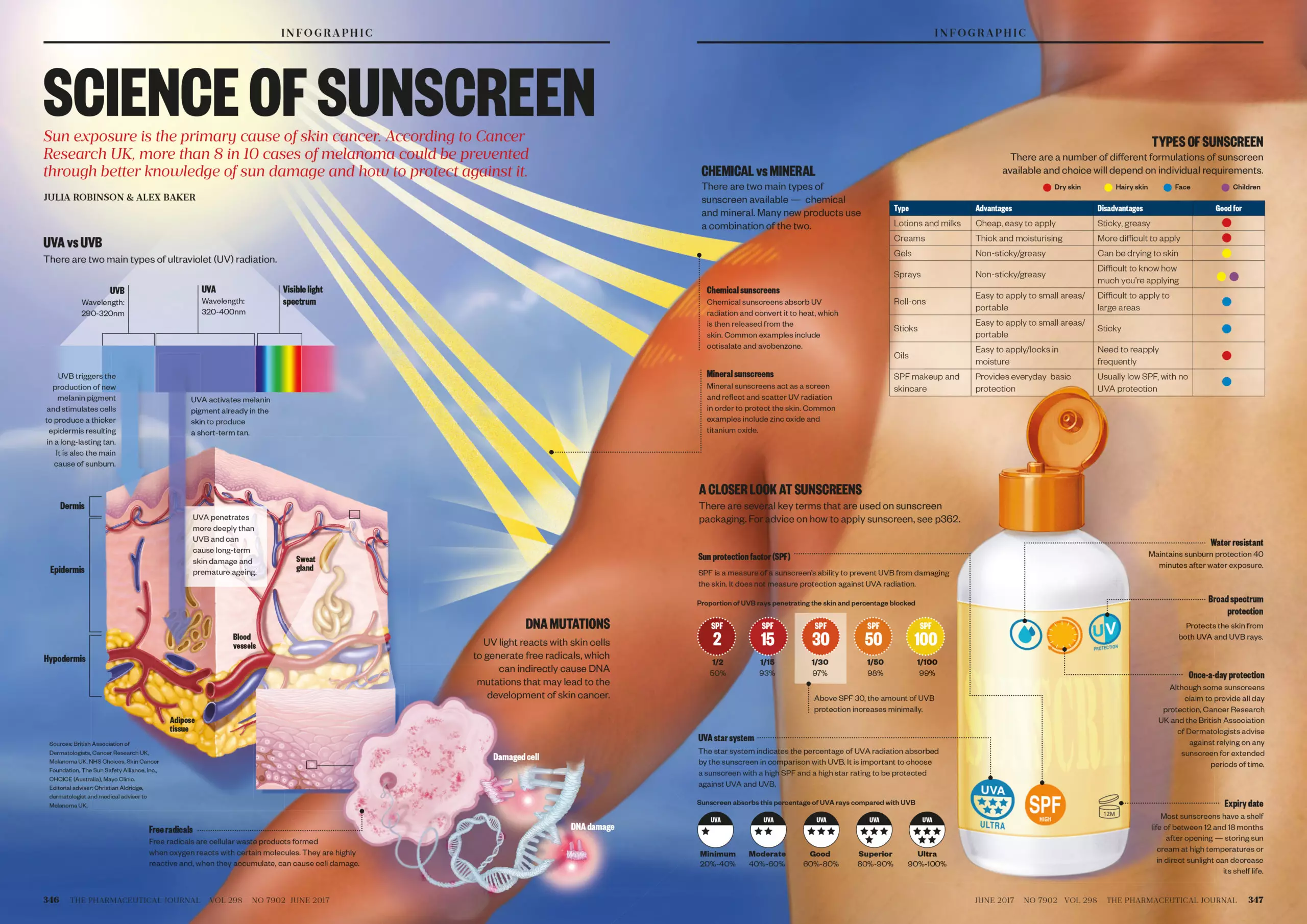
UV radiation, a component of sunlight, is categorized into three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVC is largely absorbed by the ozone layer, while UVA and UVB reach the Earth’s surface.
- UVA penetrates deep into the skin, contributing to premature aging, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation. It also plays a role in the development of skin cancer.
- UVB is primarily responsible for sunburns and plays a significant role in the development of skin cancer.
The Unprotected Skin: A Vulnerable Canvas
Without sunscreen, our skin is directly exposed to the damaging effects of UV radiation. This exposure can lead to a cascade of detrimental effects:
- Sunburns: The most immediate consequence of excessive UVB exposure, sunburns are characterized by redness, pain, and inflammation. Repeated sunburns significantly increase the risk of skin cancer.
- Premature Aging: UVA rays penetrate deeper into the skin, breaking down collagen and elastin, the proteins responsible for skin elasticity and firmness. This leads to wrinkles, fine lines, and uneven skin tone.
- Hyperpigmentation: Sun exposure can trigger the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. This can lead to dark spots, freckles, and uneven skin tone.
- Skin Cancer: UV radiation can damage DNA in skin cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and the development of skin cancer. The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Sunscreen: A Protective Barrier Against the Sun’s Harmful Rays
Sunscreen acts as a shield, absorbing or reflecting UV radiation before it reaches the skin. It contains specific chemical filters that absorb UV rays and release them as heat, or physical filters that create a barrier on the skin to reflect UV rays.
The Power of SPF: Measuring Sunscreen Protection
The Sun Protection Factor (SPF) indicates a sunscreen’s ability to protect against UVB rays. An SPF of 15 blocks approximately 93% of UVB rays, while an SPF of 30 blocks about 97%. Higher SPF values offer increased protection, but it is crucial to understand that no sunscreen can block 100% of UV radiation.
Beyond SPF: Understanding Broad Spectrum Protection
While SPF measures protection against UVB rays, it’s equally important to choose sunscreens that offer broad-spectrum protection, safeguarding against both UVA and UVB rays. This ensures comprehensive protection from the sun’s harmful effects.
Applying Sunscreen: A Crucial Step in Sun Protection
Sunscreen application is crucial to maximize its effectiveness. Here are some key guidelines:
- Apply liberally: Use a generous amount of sunscreen, enough to cover the entire exposed skin area.
- Reapply frequently: Reapply sunscreen every two hours, especially after swimming, sweating, or towel drying.
- Protect sensitive areas: Pay close attention to areas like the face, ears, neck, and hands, which are often exposed.
- Start early: Begin using sunscreen in childhood to develop healthy sun protection habits.
The Importance of Consistency: A Daily Ritual for Skin Health
Sunscreen should be incorporated into a daily skincare routine, even on cloudy days, as UV rays can penetrate clouds. This consistent approach provides long-term protection against the sun’s damaging effects.
Beyond Sunscreen: Complementing Sun Protection
While sunscreen is a crucial component of sun protection, it’s essential to adopt a comprehensive approach:
- Seek shade: During peak sun hours (10 am to 4 pm), seek shade whenever possible.
- Wear protective clothing: Opt for clothing made from tightly woven fabrics that block UV rays.
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat: Hats provide additional protection for the face, ears, and neck.
- Wear sunglasses: Sunglasses shield the eyes from harmful UV rays, reducing the risk of cataracts and other eye conditions.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Sunscreen
Q: Can I use expired sunscreen?
A: Expired sunscreen may not be as effective in protecting your skin. It’s best to discard sunscreen after the expiration date and replace it with fresh product.
Q: Is sunscreen necessary on cloudy days?
A: Yes, UV rays can penetrate clouds, so sunscreen is essential even on cloudy days.
Q: Can I use sunscreen under makeup?
A: Yes, many sunscreens are specifically formulated to be used under makeup. Look for lightweight, non-comedogenic formulas.
Q: How long does it take for sunscreen to work?
A: Sunscreen should be applied 20 minutes before sun exposure to allow it to fully absorb into the skin.
Q: Can I use sunscreen on my face?
A: Yes, there are many sunscreens specifically designed for the face, formulated to be gentle on sensitive skin.
Q: Can I use sunscreen on children?
A: Yes, it’s essential to protect children’s delicate skin from the sun. Choose sunscreens specifically formulated for children.
Tips: Enhancing Sun Protection Practices
- Choose the right sunscreen: Consider your skin type, activity level, and the amount of sun exposure you anticipate.
- Check the ingredients: Opt for sunscreens with broad-spectrum protection and SPF 30 or higher.
- Store sunscreen properly: Store sunscreen in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight.
- Educate yourself: Stay informed about sun safety and the latest recommendations from dermatologists.
- Be a role model: Encourage children and teenagers to use sunscreen regularly and practice sun-safe behaviors.
Conclusion: Embracing a Sun-Smart Lifestyle
The sun’s rays, while offering warmth and vitamin D, can also pose a significant threat to our skin. By embracing a sun-smart lifestyle that includes regular sunscreen use, seeking shade, wearing protective clothing, and adopting other preventive measures, we can minimize the risks associated with UV radiation and safeguard our skin health for a lifetime. Remember, protecting our skin is an investment in our present and future well-being.





![[Sun care] Why sunscreen is important! : r/SkincareAddiction](https://i.redd.it/vhroulf0fhi31.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Sun’s Embrace: Understanding the Impact of Sunscreen on Skin Health. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!