Unraveling the Complexities of Skin: A 3D Model Approach
Related Articles: Unraveling the Complexities of Skin: A 3D Model Approach
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Complexities of Skin: A 3D Model Approach. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Complexities of Skin: A 3D Model Approach
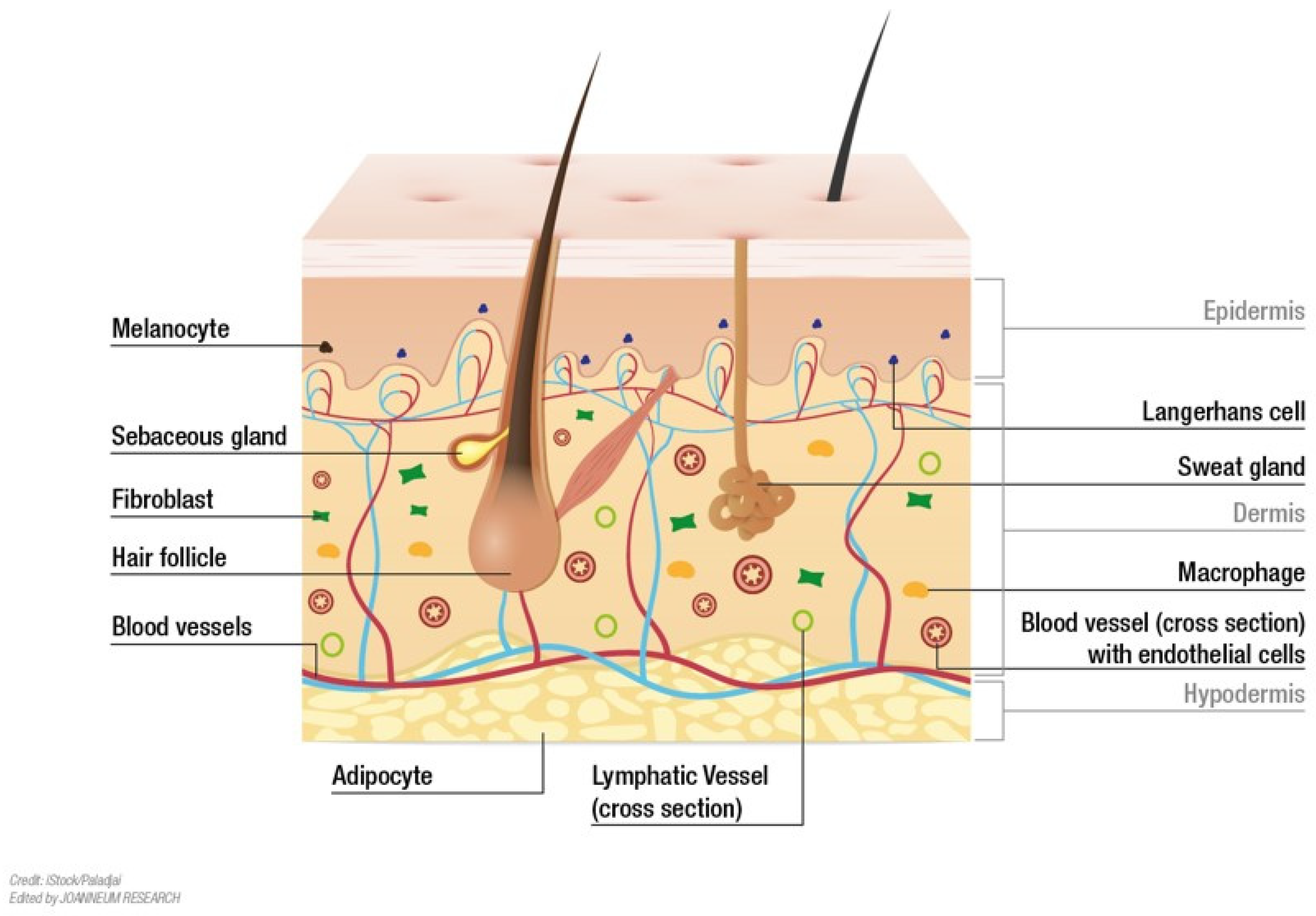
The human skin, our largest organ, is a remarkable structure that serves as a protective barrier, regulates temperature, and facilitates sensory perception. Its intricate composition, however, presents a challenge to understanding its complex functions. This is where 3D models come into play, providing a powerful tool for visualizing and exploring the intricate layers of the skin and their interactions.
The Power of Visualization: Understanding Skin Structure in 3D
Traditional 2D diagrams, while informative, often struggle to capture the true complexity of the skin’s three-dimensional architecture. 3D models, on the other hand, offer a revolutionary approach to studying skin structure, allowing researchers and educators to:
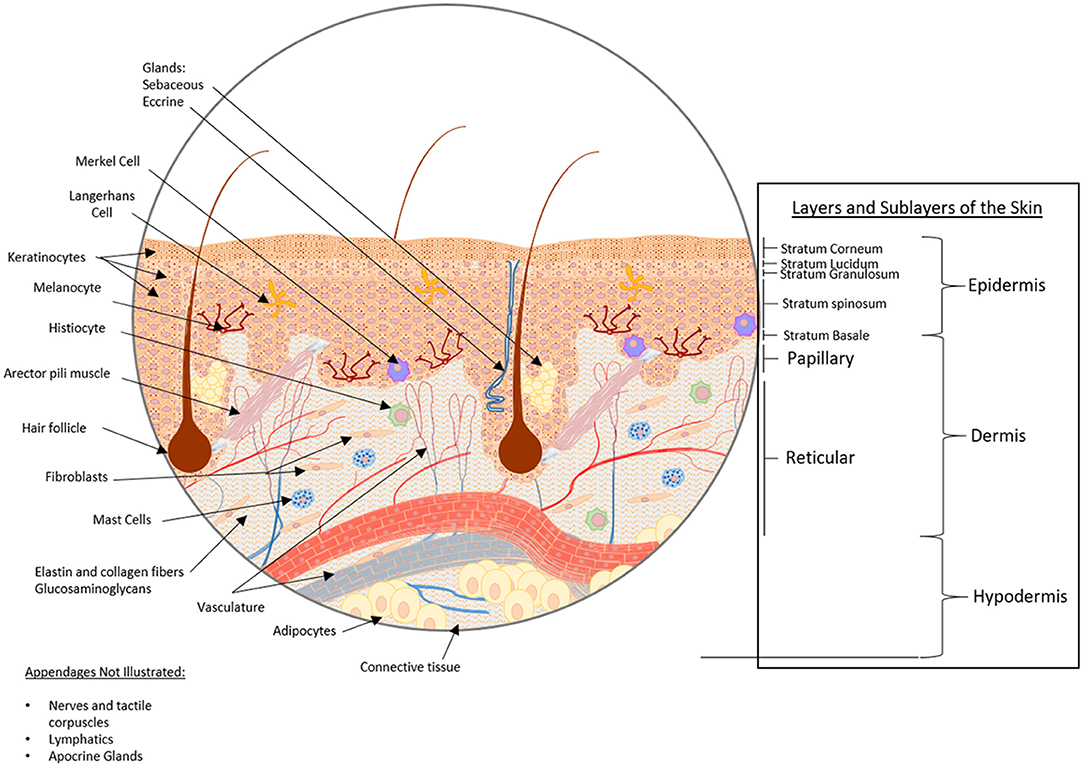
- Visualize the intricate relationships between different skin layers: 3D models provide a spatial understanding of how the epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous fat layer are interconnected, highlighting the intricate network of blood vessels, nerves, and glands that permeate the skin.
- Explore the microscopic details of skin cells: By zooming in on individual layers, 3D models enable a detailed examination of the different cell types present, such as keratinocytes, melanocytes, and fibroblasts, and their respective roles in maintaining skin health.
- Simulate the dynamic processes occurring within the skin: 3D models can be used to simulate the movement of substances through the skin, the growth and differentiation of cells, and the response of the skin to external stimuli, such as UV radiation or wound healing.
Benefits of 3D Skin Models in Research and Education
The application of 3D models in skin research and education offers a multitude of benefits:
- Enhanced comprehension of skin biology: 3D models provide a more intuitive and engaging way to learn about the complex functions of the skin, fostering deeper understanding and knowledge retention.
- Improved communication and collaboration: 3D models facilitate communication between researchers, clinicians, and educators, providing a shared visual language for discussing complex concepts and promoting collaborative research.
- Accelerated drug development and testing: By creating virtual models of the skin, researchers can test the efficacy and safety of new drugs and therapies, reducing the need for animal testing and expediting the development of new treatments.
- Personalized medicine and patient education: 3D models can be used to create customized representations of individual patients’ skin, providing insights into their specific skin conditions and facilitating personalized treatment plans.
Types of 3D Skin Models: A Spectrum of Options
The field of 3D skin modeling encompasses a diverse range of approaches, each with its own strengths and limitations:
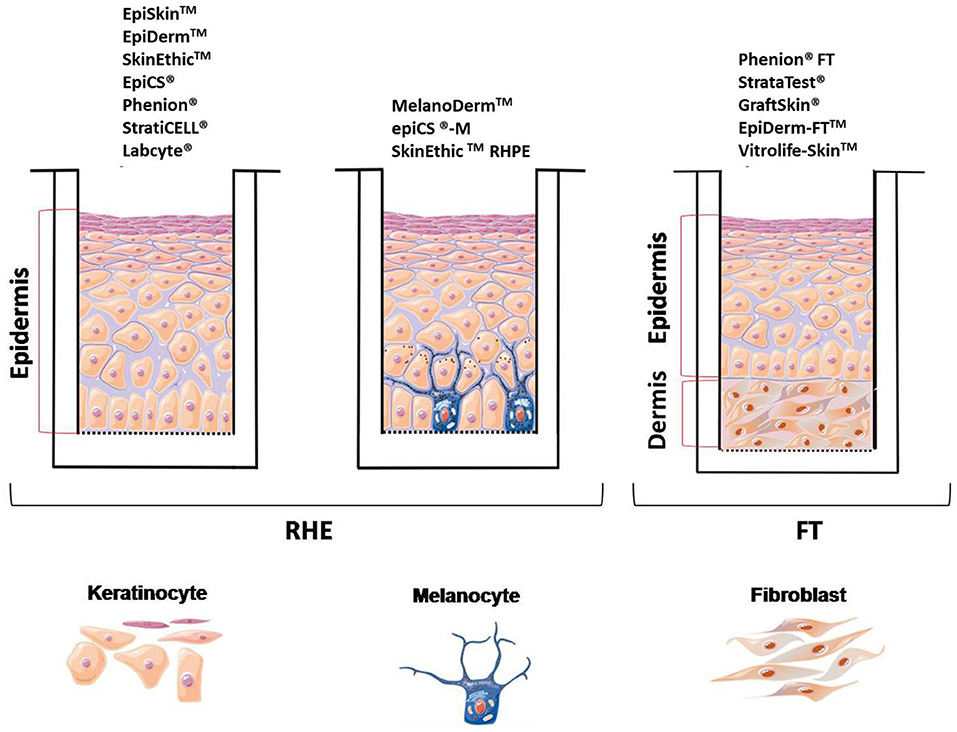
- Computer-generated models: These models are created using software programs and rely on existing knowledge of skin anatomy and physiology. They offer flexibility in terms of customization and visualization but lack the biological complexity of real tissue.
- In vitro models: These models utilize cultured skin cells or tissues grown in a laboratory setting. They offer a more realistic representation of skin function but may not fully capture the complexity of the entire organ.
- Organ-on-a-chip models: These models integrate living cells with microfluidic devices, mimicking the microenvironment of the skin. They offer a high level of biological relevance but are more complex to develop and maintain.
- 3D bioprinting: This technology utilizes biocompatible materials and living cells to create three-dimensional structures that closely resemble the skin. It offers the potential to create highly personalized and functional skin models but is still under development.
FAQs about 3D Skin Models:
1. What are the limitations of 3D skin models?
While 3D models offer significant advantages, they also have limitations. Computer-generated models may lack biological accuracy, while in vitro models may not fully capture the complexity of the entire organ. Additionally, the development of 3D bioprinted models is still in its early stages and requires further refinement.
2. How are 3D skin models used in drug development?
3D skin models can be used to test the efficacy and safety of new drugs and therapies. By simulating the human skin environment, researchers can assess how drugs penetrate the skin, their potential toxicity, and their effectiveness in treating skin conditions.
3. Can 3D skin models be used for personalized medicine?
Yes, 3D skin models can be used to create customized representations of individual patients’ skin, providing insights into their specific skin conditions and facilitating personalized treatment plans. This approach holds immense potential for improving patient outcomes and optimizing treatment strategies.
Tips for Using 3D Skin Models Effectively:
- Choose the right model for your research question: Consider the specific needs of your research and select a model that best aligns with your objectives.
- Validate the model: Ensure that the model accurately reflects the relevant aspects of skin biology and function.
- Use appropriate visualization techniques: Utilize visualization tools and techniques that effectively communicate the key features and insights of the model.
- Collaborate with experts: Engage with researchers and clinicians with expertise in skin biology and 3D modeling to enhance the validity and interpretation of your findings.
Conclusion: A New Frontier in Skin Research
3D skin models represent a transformative approach to understanding the complexities of this vital organ. By providing a powerful visualization tool, these models offer a deeper insight into skin biology, accelerate drug development, and pave the way for personalized medicine. As the field continues to advance, 3D skin models will undoubtedly play a central role in unlocking the secrets of the skin and revolutionizing the way we treat skin diseases.


/Skin%20Science%20Unraveling%20the%20Complexities%20of%20Human%20Skin.webp#keepProtocol)


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Complexities of Skin: A 3D Model Approach. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!